What components and modules does a capacitor wiring diagram contain?
What Components and Modules Does a Capacitor Wiring Diagram Contain?
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in electrical engineering, playing a crucial role in various circuits and applications. A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field, allowing it to release that energy when needed. Understanding how to read and interpret capacitor wiring diagrams is essential for engineers, technicians, and hobbyists alike. This article aims to explore the components and modules found in capacitor wiring diagrams, providing insights into their functions and applications.
II. Overview of Capacitors
A. Basic Function of Capacitors
Capacitors serve several key functions in electrical circuits. They can store energy, filter signals, smooth out voltage fluctuations, and even act as timing elements in oscillators. When a voltage is applied across a capacitor, it accumulates charge, which can be released when the circuit requires it. This ability to store and release energy makes capacitors invaluable in various applications.
B. Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
1. **Electrolytic Capacitors**: These capacitors are polarized and typically used in power supply circuits due to their high capacitance values. They are often found in applications requiring significant energy storage.
2. **Ceramic Capacitors**: Known for their stability and reliability, ceramic capacitors are commonly used in high-frequency applications. They are non-polarized and come in various capacitance values.
3. **Film Capacitors**: These capacitors use a thin plastic film as the dielectric material. They are known for their low loss and high stability, making them suitable for audio and RF applications.
4. **Tantalum Capacitors**: Tantalum capacitors are also polarized and offer high capacitance in a small package. They are often used in compact electronic devices.
C. Applications of Capacitors in Circuits
Capacitors are used in a wide range of applications, including power supply filtering, signal coupling and decoupling, timing circuits, and energy storage in power electronics. Their versatility makes them essential in both consumer electronics and industrial applications.
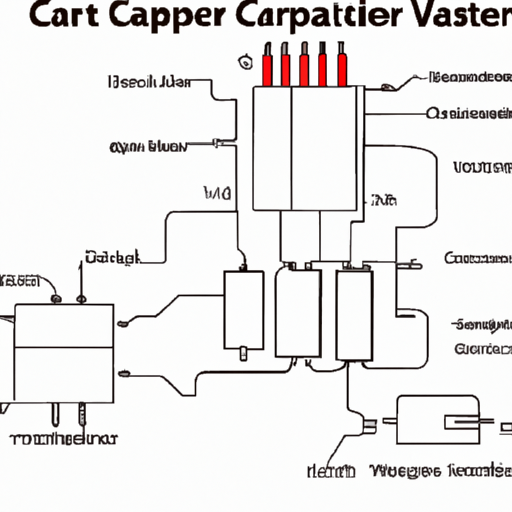
III. Components of a Capacitor Wiring Diagram
A. Capacitor Symbols
In wiring diagrams, capacitors are represented by specific symbols. The standard symbol for a capacitor is two parallel lines, with one line often curved to indicate a polarized capacitor. Variations exist based on the type of capacitor, such as the inclusion of a "+" sign for electrolytic capacitors.
B. Power Source
A power source is a critical component in any circuit involving capacitors. It provides the voltage necessary to charge the capacitor. In wiring diagrams, power sources are typically represented by a battery or a power supply symbol, indicating the connection to the capacitor.
C. Resistors
Resistors are often included in capacitor circuits to control the charging and discharging rates of capacitors. They limit the current flowing into the capacitor, preventing damage and ensuring proper operation. In wiring diagrams, resistors are represented by a zigzag line.
D. Inductors
Inductors can work in conjunction with capacitors to form resonant circuits. They store energy in a magnetic field and can influence the behavior of the circuit. In wiring diagrams, inductors are represented by a series of loops or coils.
E. Switches
Switches are essential for controlling the flow of current in capacitor circuits. They allow users to open or close the circuit, enabling or disabling the capacitor's function. In diagrams, switches are typically represented by a break in the line, indicating their open or closed state.
F. Diodes
Diodes protect capacitors from reverse polarity and voltage spikes. They allow current to flow in one direction only, safeguarding the capacitor from damage. In wiring diagrams, diodes are represented by a triangle pointing towards a line.
G. Connectors and Terminals
Connectors and terminals are crucial for establishing connections between components in a circuit. They ensure that the capacitor is properly integrated into the circuit. In diagrams, connectors are often represented by dots or circles where lines meet.
IV. Modules in a Capacitor Wiring Diagram
A. Circuit Modules
Circuit modules are sections of a wiring diagram that represent specific functions or components. For example, a power supply module may include a transformer, rectifier, and filter capacitors. Understanding these modules helps in analyzing the overall circuit design.
B. Filter Circuits
Capacitors are commonly used in filter circuits to remove unwanted frequencies from signals. There are several types of filter circuits:
1. **Low-Pass Filters**: These circuits allow low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency signals. Capacitors are used to block high frequencies.
2. **High-Pass Filters**: In contrast, high-pass filters allow high-frequency signals to pass while blocking low frequencies. Capacitors are placed in series with the load.
3. **Band-Pass Filters**: These circuits allow a specific range of frequencies to pass while blocking others. They combine both low-pass and high-pass configurations.
C. Timing Circuits
Capacitors play a vital role in timing applications, where they determine the time intervals for circuit operations. A common example is the 555 timer circuit, which uses a capacitor to control the timing of output signals. The charging and discharging of the capacitor dictate the timing intervals.
D. Oscillator Circuits
In oscillator circuits, capacitors are used to create oscillations or repetitive signals. They work in conjunction with inductors to form LC oscillators or with resistors to create RC oscillators. These circuits are essential in generating clock signals for digital devices.
V. Reading and Interpreting Capacitor Wiring Diagrams
A. Understanding the Layout of a Wiring Diagram
Wiring diagrams are organized representations of electrical circuits, showing how components are connected. Understanding the layout is crucial for interpreting the diagram accurately. Components are typically arranged logically, with power sources at the top and outputs at the bottom.
B. Identifying Components and Their Functions
When reading a wiring diagram, it's essential to identify each component and understand its function within the circuit. Familiarity with symbols and their meanings will aid in this process.
C. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Reading Diagrams
Common mistakes include misinterpreting symbols, overlooking connections, and failing to recognize the flow of current. Taking the time to study the diagram carefully can help avoid these pitfalls.
VI. Practical Applications of Capacitor Wiring Diagrams
A. Real-World Examples of Capacitor Wiring Diagrams
Capacitor wiring diagrams are prevalent in various applications, from simple electronic devices to complex industrial systems. Examples include power supply circuits, audio equipment, and motor control systems.
B. Importance in Troubleshooting and Repairs
Understanding capacitor wiring diagrams is invaluable for troubleshooting and repairing electronic devices. Technicians can quickly identify faulty components and determine the necessary repairs.
C. Role in Circuit Design and Development
For engineers and designers, capacitor wiring diagrams are essential tools in the development of new circuits. They provide a clear representation of how components interact, facilitating the design process.
VII. Conclusion
Understanding the components and modules found in capacitor wiring diagrams is crucial for anyone involved in electrical engineering. These diagrams serve as blueprints for designing, troubleshooting, and repairing circuits. As technology continues to evolve, the role of capacitors remains significant, making it essential for engineers and enthusiasts to deepen their knowledge in this area.
VIII. References
For further learning, consider exploring the following resources:
- "The Art of Electronics" by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill
- Online courses on platforms like Coursera and edX focusing on electrical engineering
- Websites such as Electronics Tutorials and All About Circuits for practical examples and explanations
By delving into the world of capacitors and their wiring diagrams, you can enhance your understanding of electrical circuits and their applications in modern technology.