Capacitors are what are the important product categories of capacitors?
Capacitors: Important Product Categories and Their Significance
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in storing and releasing electrical energy. They are essential for various applications, from smoothing out voltage fluctuations to filtering signals in audio equipment. This blog post aims to explore the different product categories of capacitors, their characteristics, applications, and the emerging trends in capacitor technology.
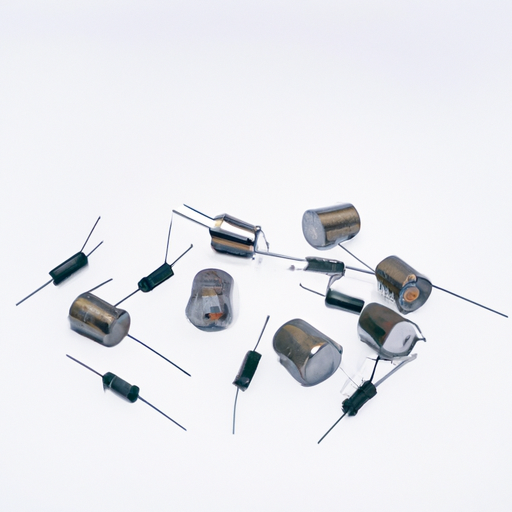
II. Types of Capacitors
Capacitors can be classified based on their dielectric material, which significantly influences their performance and applications. Here are the primary types of capacitors:
A. Ceramic Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Ceramic capacitors are made from ceramic materials and are known for their small size, low cost, and stability. They typically have a high capacitance-to-volume ratio and can operate at high frequencies.
**Applications:**
These capacitors are widely used in decoupling and filtering applications in electronic circuits, such as power supply circuits, RF circuits, and timing circuits. Their reliability and performance make them a popular choice in consumer electronics.
B. Electrolytic Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized components that offer high capacitance values in a relatively small package. They are typically made with an electrolyte and have a higher voltage rating compared to other types.
**Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly used in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and energy storage applications. Their ability to store large amounts of energy makes them ideal for smoothing out voltage fluctuations in power supplies.
C. Film Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Film capacitors use a thin plastic film as the dielectric material. They are known for their stability, low ESR, and excellent performance over a wide temperature range.
**Applications:**
Film capacitors are often used in applications requiring high precision and reliability, such as audio equipment, power electronics, and timing circuits. They are also favored in applications where low losses are critical.
D. Tantalum Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Tantalum capacitors are known for their high capacitance values and small size. They are also polarized and have a stable capacitance over a wide temperature range.
**Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly used in compact electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, where space is limited. They are also used in power supply circuits and applications requiring high reliability.
E. Supercapacitors
**Characteristics:**
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, have extremely high capacitance values and can store large amounts of energy. They can charge and discharge rapidly, making them suitable for applications requiring quick bursts of power.
**Applications:**
Supercapacitors are used in energy storage systems, backup power supplies, and regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles. Their ability to bridge the gap between traditional capacitors and batteries makes them increasingly popular in various applications.
III. Capacitor Specifications
When selecting a capacitor, several specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance in a given application:
A. Capacitance Value
The capacitance value, measured in farads (F), indicates the amount of electrical charge a capacitor can store. It is essential to choose a capacitor with the appropriate capacitance for the specific application.
B. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage a capacitor can handle without breaking down. Exceeding this rating can lead to capacitor failure, so it is crucial to select a capacitor with a voltage rating higher than the maximum voltage in the circuit.
C. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in capacitance value. It is expressed as a percentage and is important for applications requiring precise capacitance values.
D. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient indicates how the capacitance value changes with temperature. Different capacitor types have varying temperature coefficients, which can affect performance in temperature-sensitive applications.
E. Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
ESR is a measure of the resistance a capacitor presents to alternating current (AC). Low ESR is desirable in applications where high-frequency performance is critical, as it minimizes energy losses.
IV. Specialized Capacitor Categories
In addition to the standard types of capacitors, there are specialized categories designed for specific applications:
A. Power Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Power capacitors are designed to handle high voltages and currents. They are typically larger and have higher capacitance values than standard capacitors.
**Applications in Power Electronics:**
These capacitors are used in power factor correction, energy storage, and voltage regulation in power systems. They help improve the efficiency and stability of electrical grids.
B. Timing Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Timing capacitors are used in timing circuits and are selected for their precise capacitance values and stability.
**Applications in Timing Circuits:**
These capacitors are commonly found in oscillators, timers, and clock circuits, where accurate timing is essential.
C. Audio Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
Audio capacitors are designed to minimize distortion and maintain signal integrity in audio applications.
**Applications in Audio Equipment:**
They are used in amplifiers, crossovers, and other audio equipment to enhance sound quality and performance.
D. High-Voltage Capacitors
**Characteristics:**
High-voltage capacitors are designed to operate at voltages significantly higher than standard capacitors. They are built with robust materials to withstand high electrical stress.
**Applications in High-Voltage Systems:**
These capacitors are used in power transmission, industrial equipment, and high-voltage power supplies, where reliability and safety are paramount.
V. Emerging Trends in Capacitor Technology
As technology advances, several trends are shaping the future of capacitors:
A. Miniaturization and High-Capacity Designs
The demand for smaller, more efficient electronic devices is driving the development of miniaturized capacitors with higher capacitance values. This trend is particularly evident in consumer electronics, where space is at a premium.
B. Environmentally Friendly Capacitors
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, manufacturers are focusing on developing capacitors that are more environmentally friendly. This includes using sustainable materials and reducing the environmental impact of production processes.
C. Advancements in Supercapacitor Technology
Supercapacitors are gaining traction due to their unique properties, such as rapid charging and discharging capabilities. Ongoing research is focused on improving their energy density and reducing costs, making them more viable for a broader range of applications.
VI. Conclusion
Capacitors are vital components in modern electronic circuits, with various types and specifications tailored to meet specific needs. Understanding the different product categories, such as ceramic, electrolytic, film, tantalum, and supercapacitors, is essential for selecting the right capacitor for any application. As technology continues to evolve, emerging trends in capacitor design and materials will further enhance their performance and sustainability.
In summary, capacitors play a crucial role in the functionality of electronic devices, and their diverse applications highlight their importance in the electronics industry. The future of capacitor technology looks promising, with advancements that will continue to drive innovation and efficiency in electronic design.
VII. References
For further exploration of capacitors and their applications, consider the following resources:
1. "Capacitors: Principles and Applications" by John Smith
2. "The Art of Electronics" by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill
3. Online resources such as IEEE Xplore and Electronics Tutorials for the latest research and developments in capacitor technology.
By understanding the various types and specifications of capacitors, engineers and hobbyists alike can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and reliability of their electronic projects.